SAMPLE ANSWER Flowering plants reproduce by making seeds in flowers SAMPLE ANSWER Flowering plants produce male and female gametophytes in flowers Pollen grains transfer sperm to the stigma of a flower Double fertilization in an ovule produces a zygote and endosperm The ovule becomes a seed SAMPLE ANSWER Fruits protect seeds, and seeds grow into new plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Notes Biology in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app The best app for CBSE students now provides Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants class 12 Notes latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE board exams and schoolbased annual examinationsQ What contains one or more seeds, and develops from the ovary, and sometimes other parts of the flower?

Seed Plant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Reproduce by seeds flowering plants
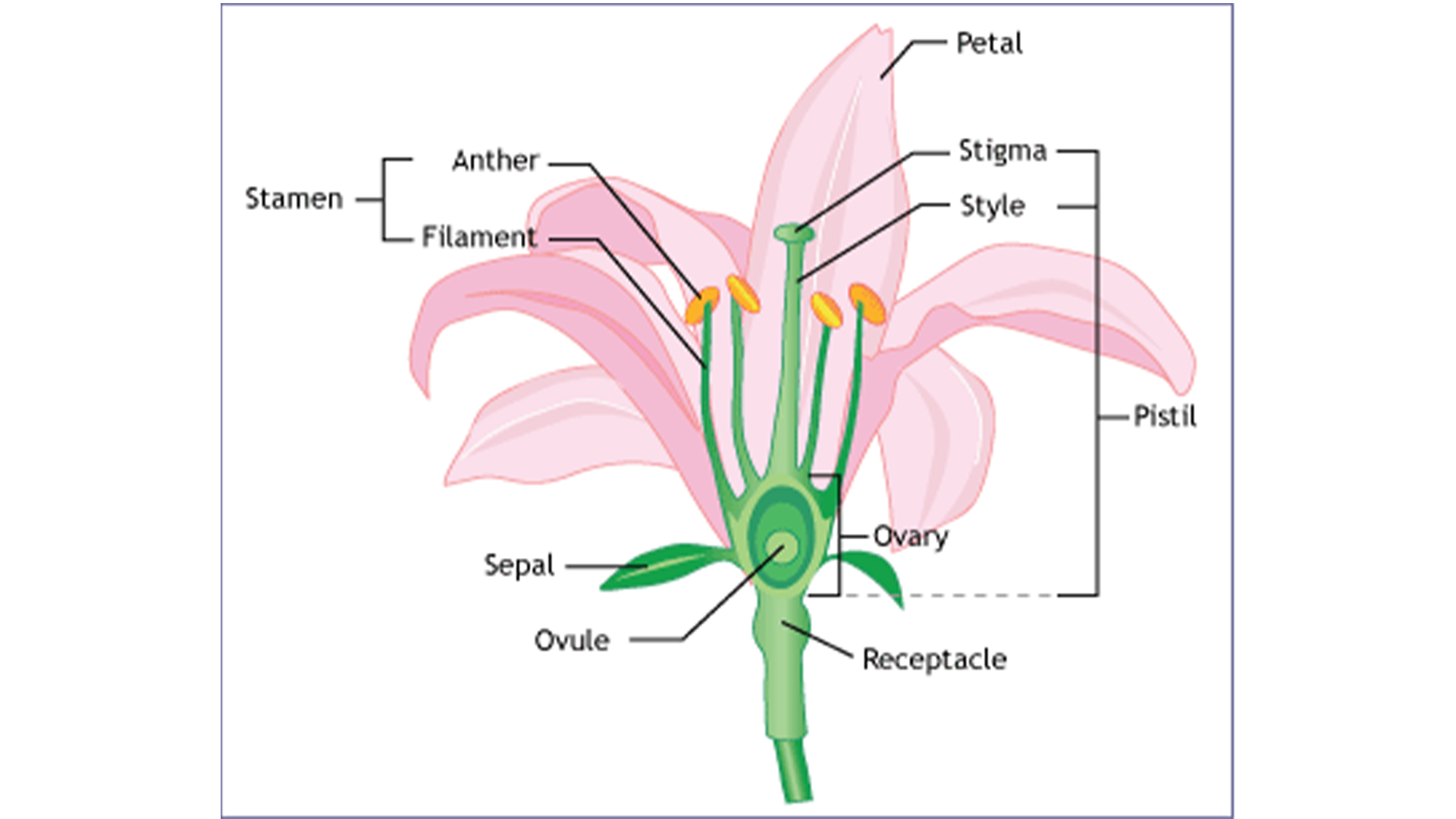
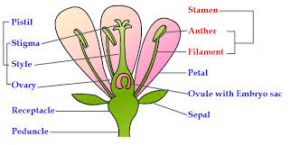
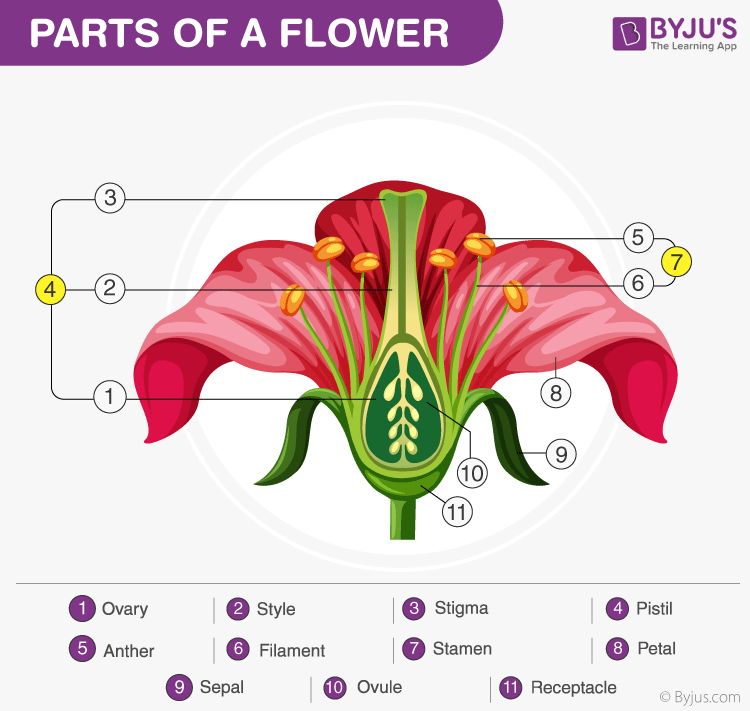
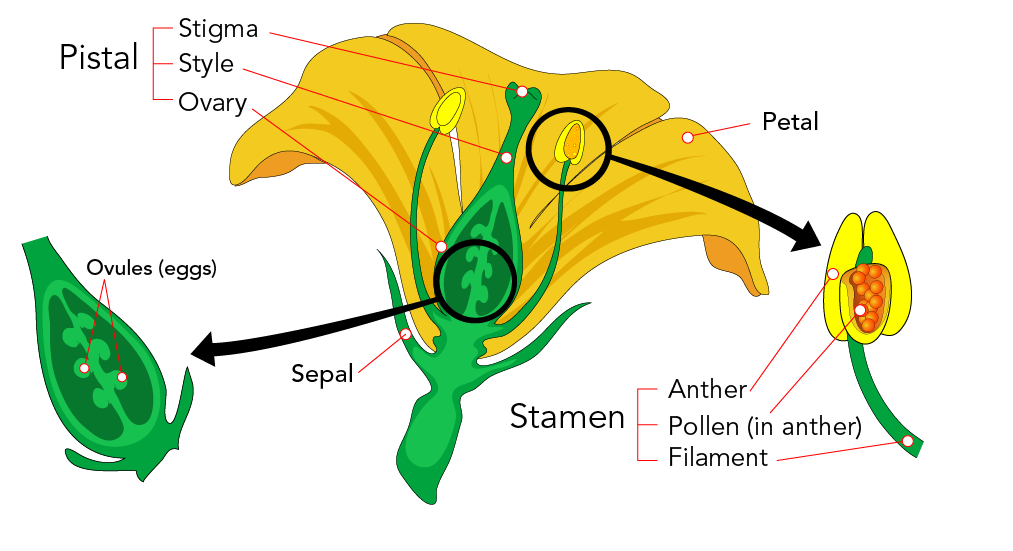
Reproduce by seeds flowering plants- Reproduction in flowering plants 2 Flower Structure PETALS These are usually brightly coloured and sometimes scented They are arranged in a circle or a cylinder The petals attract insects to the flower, the insects may bring about pollination CARPEL These are the female reproductive organs Each carpel consists of an ovary, bearing of style and a stigma Inside the Sexual reproduction is the process of development of new organisms through the formation and fusion of gametes In flowering plants, stamens are male reproductive organs while carpels are female reproductive organs In angiosperms, male and female gametes are formed in male and female sex organs by the process of meiosis



Learn About Flowering Plant Reproduction Chegg Com
Less attention is required by the plants grown through asexual means than through seeds Sexual Reproduction In Plants The reproductive parts of plants are flowers, Stamen being male reproductive part and pistil being the female reproductive part If one of these reproductive parts are present in a flower, it is said to be a unisexual flower Example papaya IfA Flowering plants reproduce through seeds B Flowering plants reproduce through other plant parts C Sexual reproduction takes place when there is fertilization D Sexual reproduction takes place when flowers produce seeds 5 Which of the following statements is TRUE about asexual reproduction inReproduction in Flowering Plants For Teachers 7th 9th Detailing the structures and functions of flowering plants, this slide show will help your students understand the processes and the conditions that allow pollination and fertilization Labelled diagrams help introduce the reproductive Get Free Access See Review Lesson Planet AP Chapter 29 and 30 Plant
Flowering plants are unusual among seed plants in their superlative exploitation of animals (primarily insects) as agents of outcross pollination The outcross pollination efficiency of insects, birds, and mammals (primarily bats) may have contributed to both the abundance and diversity of flowering plants Abundance may have increased because of less wastage of energy andReproduction in flowering plants Learning outcomes 31 understand the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction 32 understand that fertilisation involves the fusion of a male and female gamete to produce a zygote that undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo 33 describe the structures of an insectpollinated and a windpollinated flower and explain how Premeiotic 21nucleotide reproductive phasiRNAs emerged in seed plants and diversified in flowering plants Suresh Pokhrel ORCID orcidorg/ 1
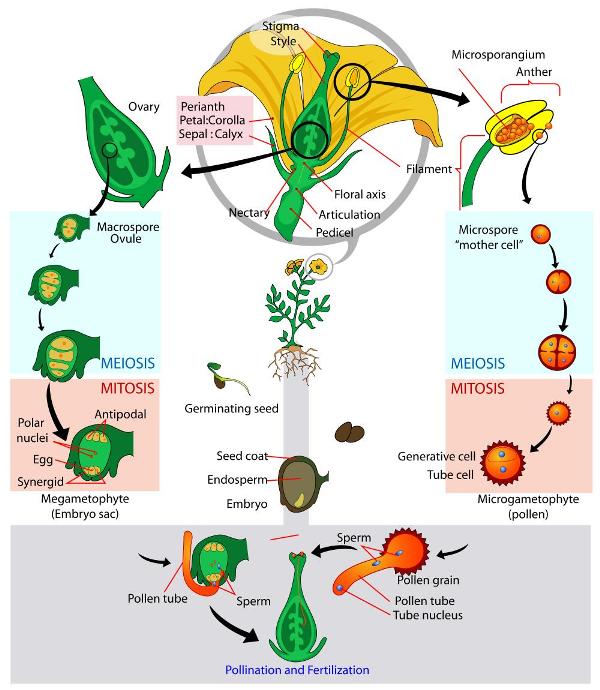
Flower parts and functions (receptacle, corolla, petals, calyx, sepals, stamen, anther, filament, pistil, stigma, style, ovary);Formation of seed C2 91 Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Learning Outcome At the end of the lesson, students should be able to •State and define the terminologies involve in gamete formation in flowering plants C1 •Male gamete microsporangium / pollen sac, microsporocyte / microspore mother cell, microspore, tetrad, pollen grain/male gametophyte, generative cell, tube In seed plants, however, the nonmotile male gametes are carried to female gamete by pollen tubes POSTFERTILIZATION EVENTS Events in sexual reproduction after the formation of zygote are called postfertilization events In organisms belonging to fungi and algae, zygote develops a thick wall that is resistant to desiccation and damage It undergoes a period of rest




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs
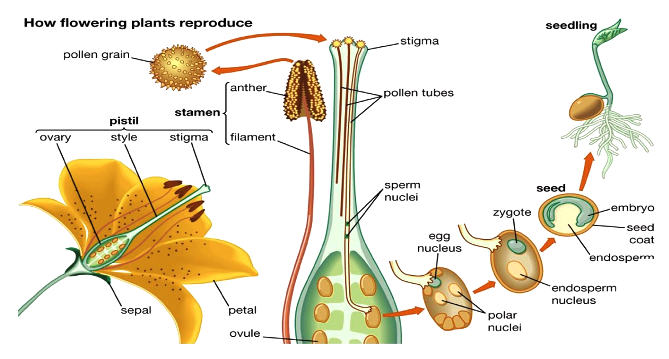
Flowering Plant Seed Reproductive Parts Flowering plants, called angiosperms, develop a fruit from the ovary wall that encloses the seeds The parts of a flower are derived from modified leaves Reproduction in flowering plants begins with the process of pollination during which the male gametes are transferred to the female ovules Following pollination, fertilization involves the growth of the pollinated ovules into seeds As the seeds develop within the fruit of the flower, the fruit ripens and the seeds are freed from the fruit to be dispersed and allowed to germinatePollination The transfer of pollen grains from an anther (male plant structure) to a stigma (female plant structure) Many plants possess both male and female structures (monoecious) and can




Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants Britannica




Plant Reproduction Flowering Plants Known As Angiosperms Covered
PLANT REPRODUCTION HOW TO CLASSIFY HUGUET FITÉ, Janet CEIP Antoni Roig Lesson 1 Name _____ Introduction How to classify Flowering plants produce true flowers The nonflowering plants include "primitive" plants, such as algae, mosses, and ferns Horsetails, and liverworts, and the "gymnosperms" a group of plants which includes the conifers There are about 3000,000One sperm's nucleus combines with the egg nucleus to produce a zygote, while the other combines with the same egg's two polar nuclei to produce the first cell of the triploid endosperm (the tissue that will nourish the growing plant embryo)Reproduction in flowering plant MCQ Pollen embryoids were discovered by (a) Guha and Maheshwari (b) Steward and White (c) Konar and Natraja (d) Nitsch and Skoog The embryo may arise either from egg or some other cell of gametophyte in (a) Vegetative reproduction (b) Recurrent apomixis




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize



Flowering Plant Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Biology MCQs Pdf Question 1 What is the function of filiform apparatus in an angiospermic embryo sac?Flowering plants, the angiosperms , were the last of the seed plant groups to evolve, appearing over 100 million years ago during the middle of the Age of Dinosaurs (late Jurassic ) All flowering plants produce flowers and if they are sexually reproductive, they produce a diploid zygote and triploid endospermFlowers, the reproductive organs of flowering plants, are the most remarkable feature distinguishing them from the other seed plants Flowers provided angiosperms with the means to have a more speciesspecific breeding system, and hence a way to evolve more readily into different species without the risk of crossing back with related species Faster speciation



Nova The Reproductive Role Of Flowers Pbs Learningmedia



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Characteristics Advantages Disadvantages
In flowering plants, the process of fertilization was discovered by Strasburger in 1841 After entering into the embryo sac, the tip of the pollen tube bursts and two male gamete are discharged One of the male gametes moves towards the egg cellConservation of reproductive 21 nt phasiRNA in seed plants propose a model of how different triggers in different species function to generate reproductive 21 nt phasiRNAs in seed and flowering plants (Fig 6b) All of these triggers starts with uracil (U) and are 22 nt in length consistent with earlier finding that only the 22 nt form of miRNAs in AGO1 complex are capable ofAsexual reproduction in plants (from roots, stems and leaves);



Reproduction In




Plant Reproduction Bioninja
In flowering plants, the flowers enable reproduction with even the parts of the flower that are sterile playing important roles Explore the reproduction and Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Microspore "Mother cell" The functional megaspore is the first cell of the female gametophyte The nucleus of megaspore divides mitotically to form 8 nuclei and give rise to embryo sac or female gametophyte This process is called megagametogenesis Out of 8 nuclei, 4 nuclei are arranged at each pole One nucleus from eachDOI / Authors Suresh Pokhrel Donald Danforth




Fire Synchronizes Flowering And Boosts Reproduction In A Widespread But Declining Prairie Species Pnas



How Seep Plants Reproduce Study Sheet Hanford Christian School Jane Kitson
Premeiotic, 21nucleotide Reproductive PhasiRNAs Emerged in Seed Plants and Diversified in Flowering Plants October ;Z state the types of pollination, their significance and various modes of pollination;Many plants also have an asexual method of reproduction Often some species, such as many orchids, are more frequently propagated vegetatively than via seeds Tubers are fleshy underground stems, as in the Irish potato Leaflets are sections of leaf will develop roots and drop off the plant, effectively cloning the plant Runners are shoots running along or over the surface




Seed Plants Evolution Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation



Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants An Overview
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Flowering plants, also called angiosperms, use a sexual mode of reproduction Reproduction in plants, mainly revolves around the flower, which has both the male and the female gametes All parts of a flower aid in the process of reproduction, although some of them are sterileA newly grown lemon plant is placed next to the parent plant that produced the seedThe two plants prove identical, indicating it was an apomictic seedWhat else can be said about this seed? A new method for quantifying plant evolution reveals that after the onset of early seed plants, complexity halted for 250 million years until the diversification of




Outdoor Education School Science Camps California



Flower Anatomy Printout Enchantedlearning Com
(a) Brings about opening of the pollen tube (b) Guides the pollen tube into a synergid (c) Prevents entry of more than one pollen tube into a synergid (d) None of these Answer (b) Guides the pollen tube into a synergidAdaptations for plant reproduction and seed dispersal Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Important questions for NEET exam preparation Questions are totally based of NCERT and Precious year asked questions Answer Keys of this Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Important questions are also given at the bottom of this page Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants is associated with Biology Class 12 and




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants S Cool The Revision Website
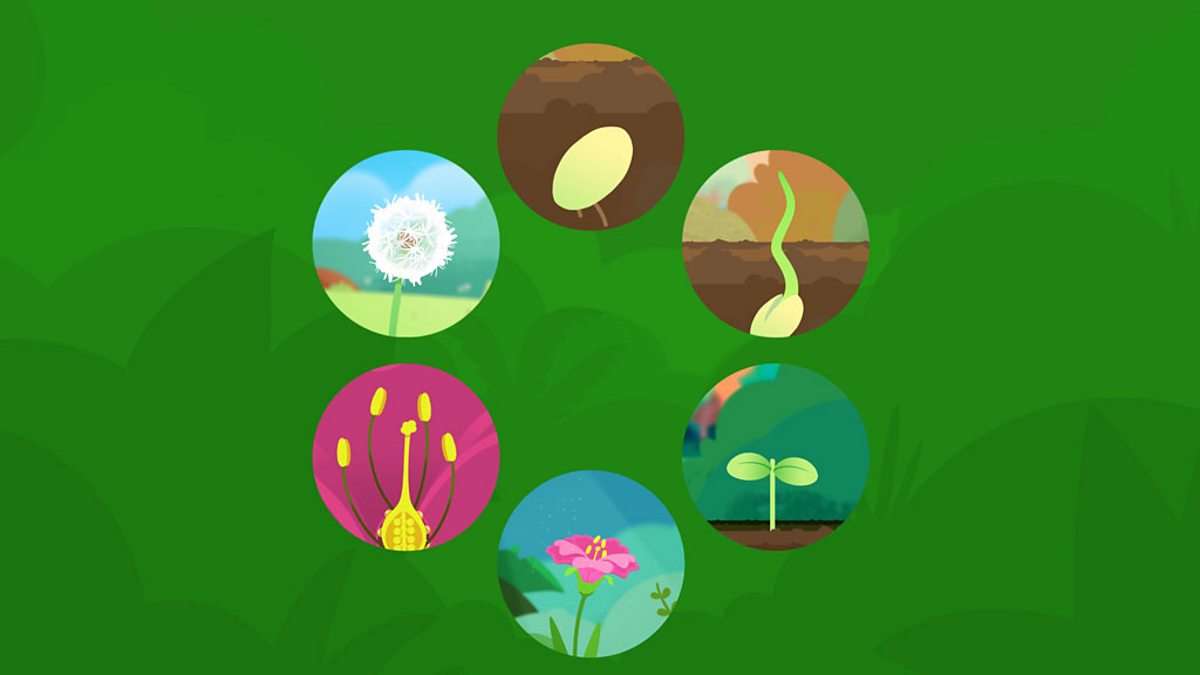
Flowering plants Sexual reproduction in flowering plants involves the production of male and female gametes, the transfer of the male gametes to the female ovules in a process called pollination After pollination occurs, fertilization happens and theFlowering plants produce seeds within a fruit The scientific name for flowering plants is angiosperms Lifecycle of a Flowering Plant Flowering plants follow a specific life cycle Seed They begin their lives as seeds Seeds are like baby plants They have a hard outer shell that protects the seed embryo inside Germination The seed ends up on the ground It needs air,Reproductive organs of monocots produce abundant phased, small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs) The 21nt reproductive phasiRNAs triggered by miR2118 are highly enriched in premeiotic anthers, and have been found in multiple eudicot species, in contrast with prior reports of monocot specificity The 24nt reproductive phasiRNAs are triggered by miR2275, and are highly




Reproduction In Flowering Plants 9 Ad Parts Of
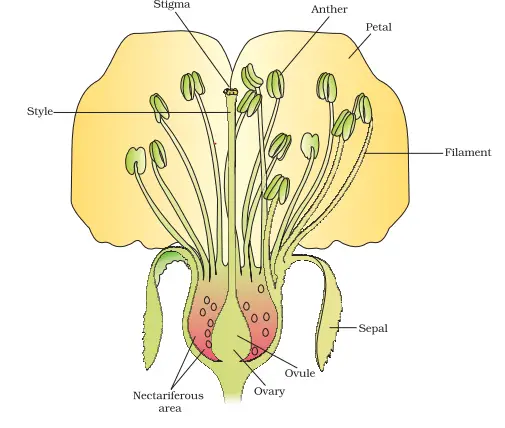



Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Notes Chapter 2 Class 12 Biology
Website http//SciencesauceonlinecomTwitter https//twittercom/science_sauceFacebook https//facebookcom/sciencesauceonline/Instagram https//wwwinstFlowering involves a change in gene expression in the shoot apex The switch to flowering is a response to the length of light and dark periods in many plants Success in plant reproduction depends on pollination, fertilization and seed dispersal Most flowering plants use mutualistic relationships with pollinators in sexual reproductionSexual reproduction in angiosperms, gymnosperms and sporebearing plants;
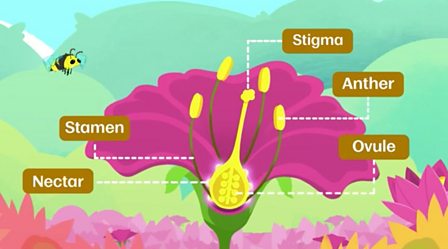



How Do Flowering Plants Reproduce c Bitesize




Flowering Plants Reproduction Fertilization Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Essential Idea Reproduction in flowering plants is influenced by the biotic and abiotic environments Outline answer to each objective statement for topic 94 (coming soon) Quizlet study set for this topic (coming soon) At SHS, Topic 94 is taught in the following class unit(s) Communities and Ecosystems (unit 24) Angiosperm Reproduction (unit 38) 94U1 FloweringLearn about plant reproduction and the process of pollination with BBC Bitesize KS3 ScienceAnswer choices flower angiosperm pollen fruit




3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download
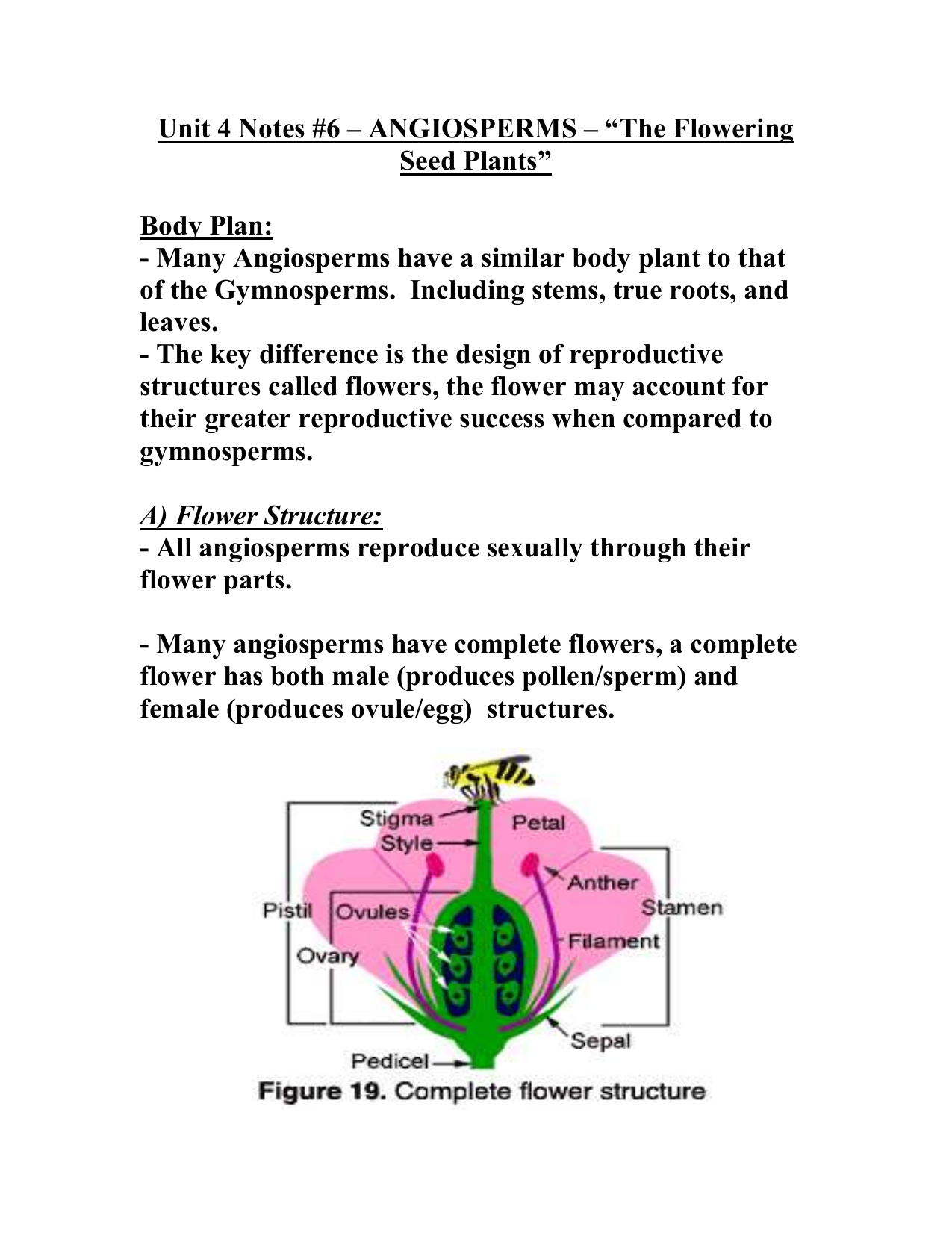



Unit 4 Notes 6 Angiosperms The Flowering Seed Plants
1st, pollen falls from a male cone onto a female cone 2nd, in time, a sperm cell and egg cell join in an ovule on the female cone 3, after fertilization occurs, the seed develops on the scale of the female cone angiosperm fertilization Gymnosperm seed developmentSexual reproduction in flowering plants involves the transfer of pollen (male gamete) to an ova (female gamete) This involves three distinct phases – pollination, fertilization and seed dispersal ;A) It was produced when two sperm fertilized one egg B) It developed from one egg alone C) It was the result of parental selffertilization D) It was homozygous for most genetic traits E) It




22 2 Reproduction In Flowering Plants Key Concept
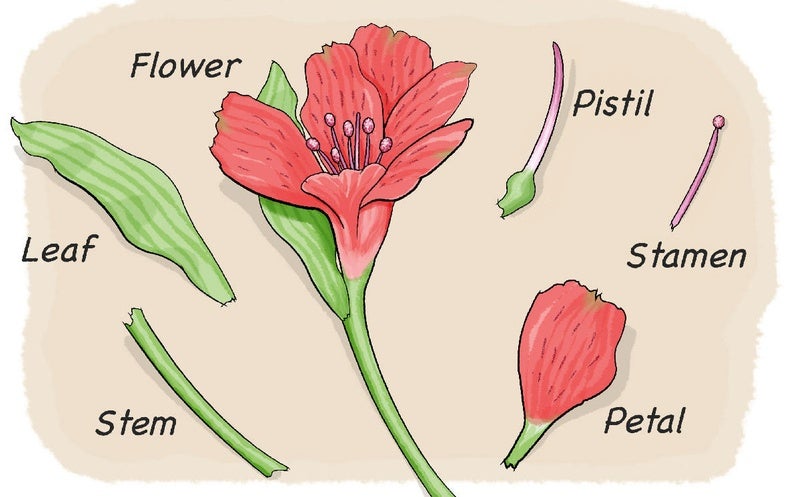



Dissect A Flower Scientific American
Reproduction in Plants 2 BIOLOGY Notes MODULE 3 Reproduction and Heredity z describe the stages of development of male and female gametophytes in flowering plants;Z explain the steps involved in fertilization, (syngamy and triple fusion), embryo development, endosperm development,
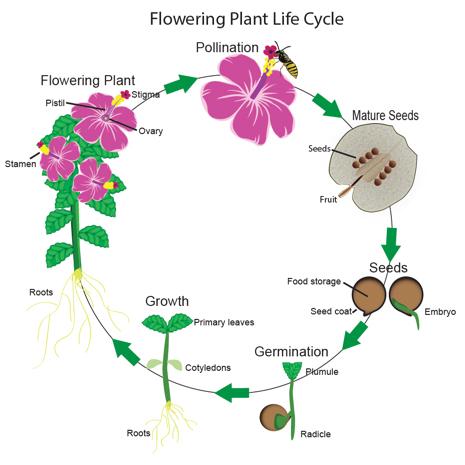



Flowering Plants Life Cycle Lovetoknow



Sexual Reproduction In Plants




Seed Plant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Sexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Biology For Kids Non Flowering Plants




Complex Body Seed Reproduction Flowering Angiosperms Stock Photo Edit Now




Flowers Or Flowers X28 Latin Flos X29 Is A Means Of Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Stock Photo Image Of Tree Angiosperms 778




Reproduction In Flowering Plants Operation Plant




Plant Reproduction In Angiosperms Flowering Plants Ppt Download
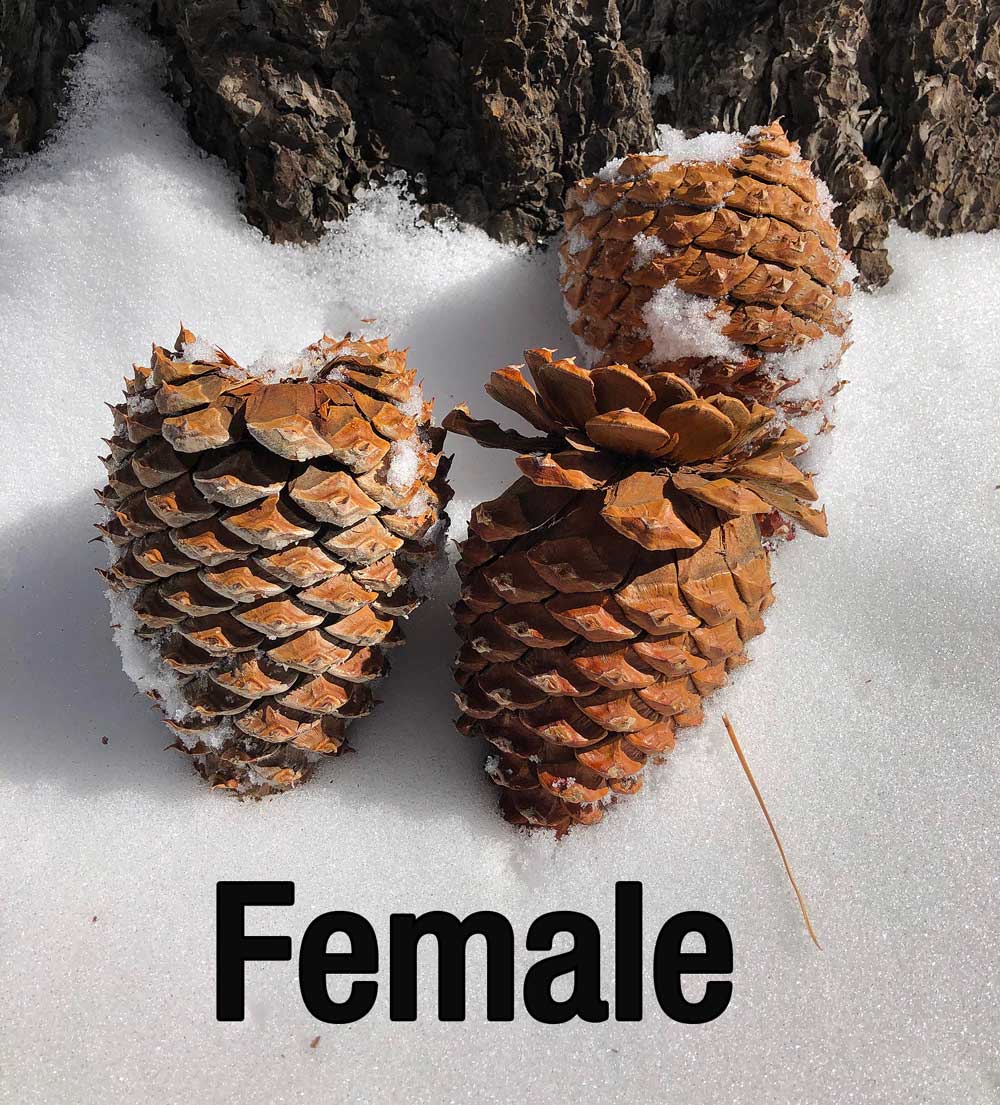




Outdoor Education School Science Camps California




Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants S Cool The Revision Website




Plant Reproduction Plants



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Flowering Seed Plant Life Cycle Diagram Quizlet



Biology For Kids Flowering Plants



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science



Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Biology Notes For Neet Aiims Jipmer
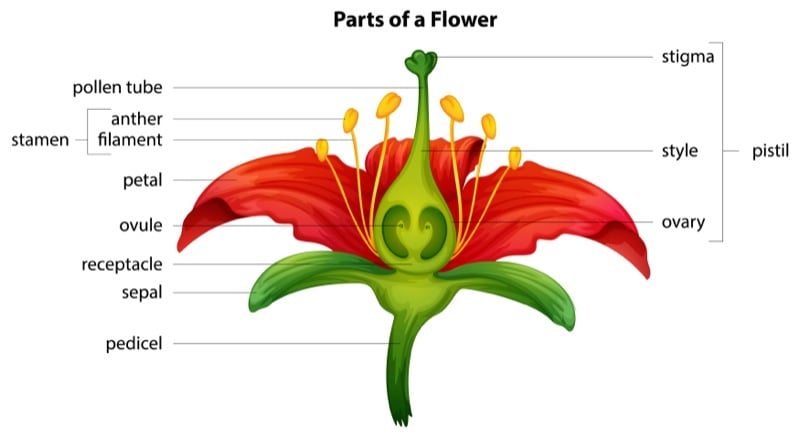



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce
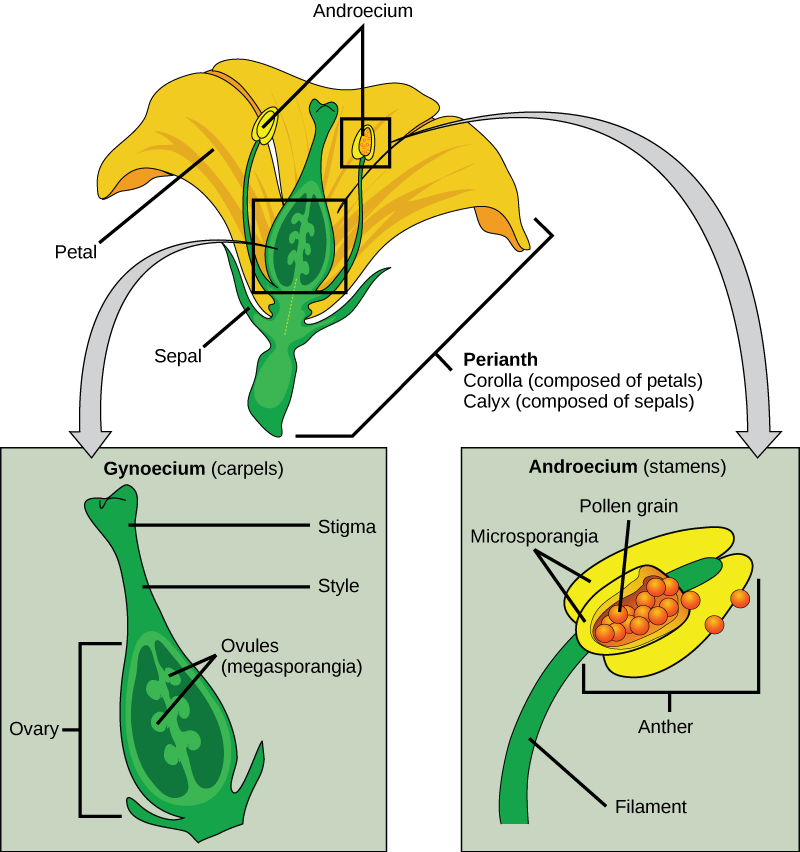



Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology
.jpg)



Flower Fruit And Seed Lessons Blendspace
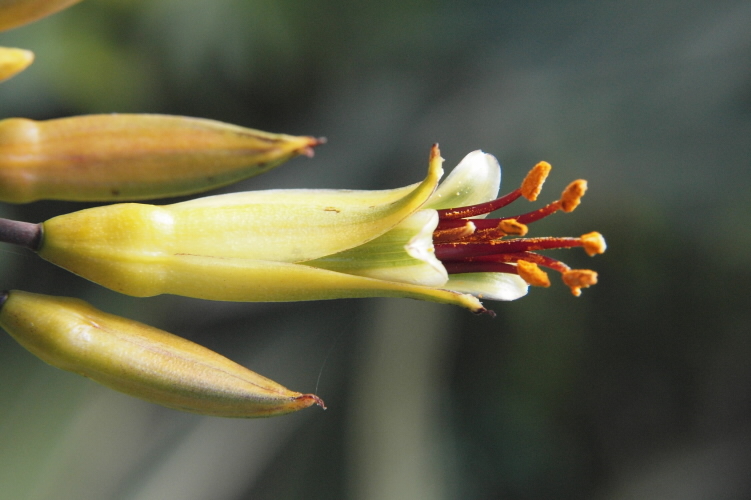




Pollination And Fertilisation Science Learning Hub
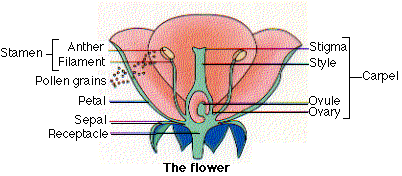



Sexual Reproduction In Angiosperms




Angiosperm Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
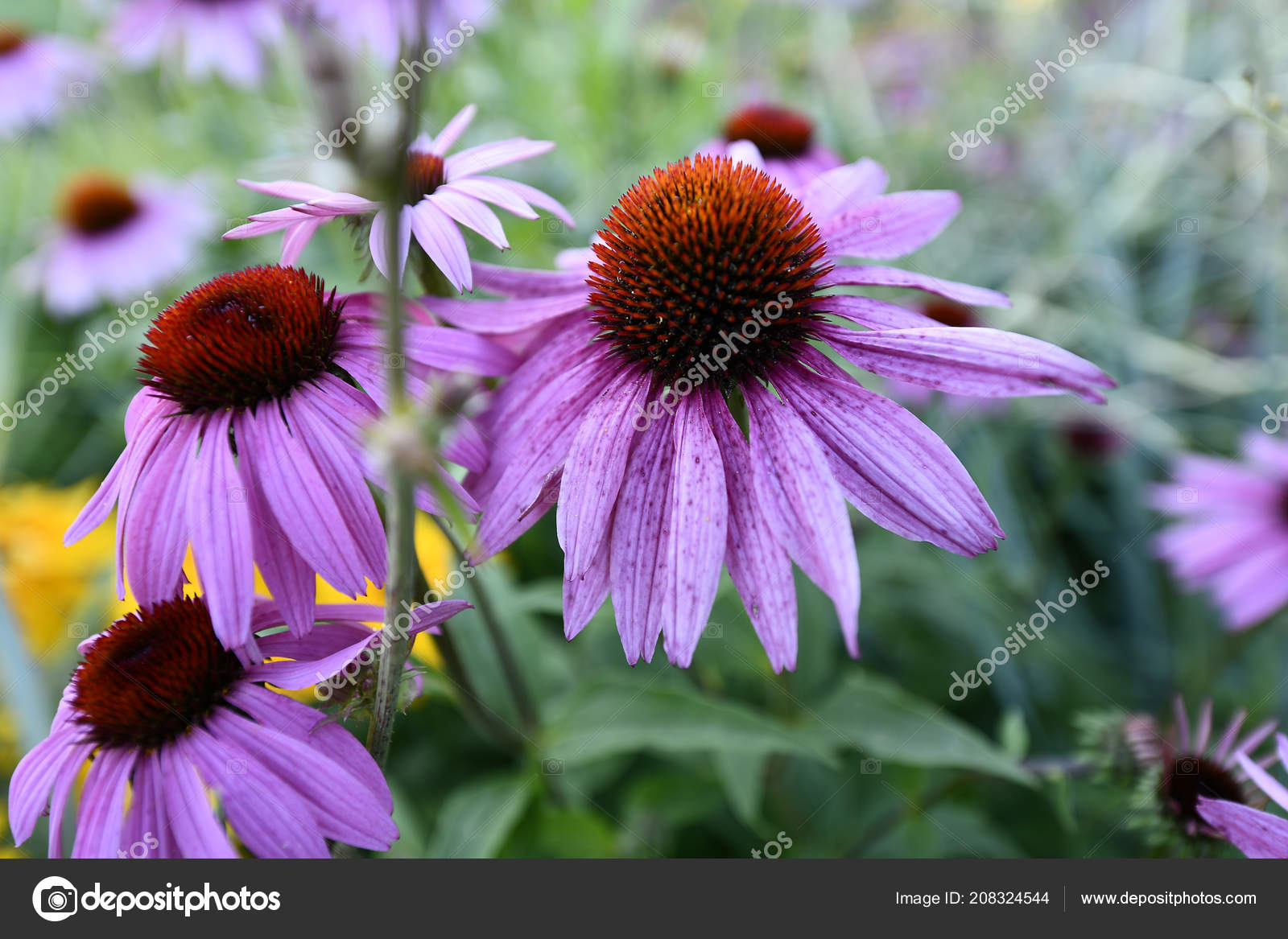




Complex Body Seed Reproduction Flowering Angiosperms Plants Stock Photo By C Enigma Art




Plant Reproduction Wikipedia




Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants By Marcella




Flowering Plant Reproduction Teachers U S National Park Service




Reach For The Sun Lesson 3 Plant Life Cycles And Reproduction Filament Games




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Science Reproduction Of Flowering Plants Lup Wai Parent Whisperer
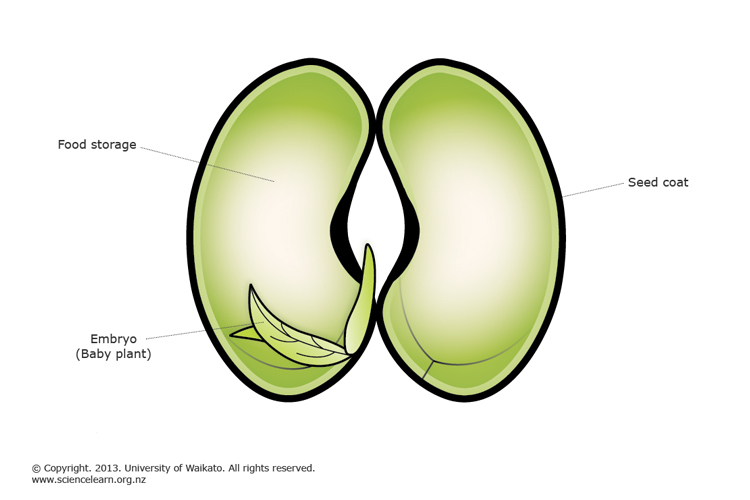



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Plant Reproductive Morphology Wikipedia




1 091 Sexual Reproduction Photos Free Royalty Free Stock Photos From Dreamstime




Beutiful Flowers Stock Image Image Of Flowers Fertilization




Mcq On Plant Reproduction By Biology Experts Notes Medium
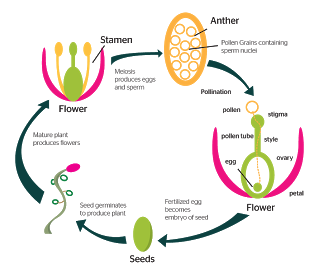



Topic 9 4 Reproduction In Plants Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
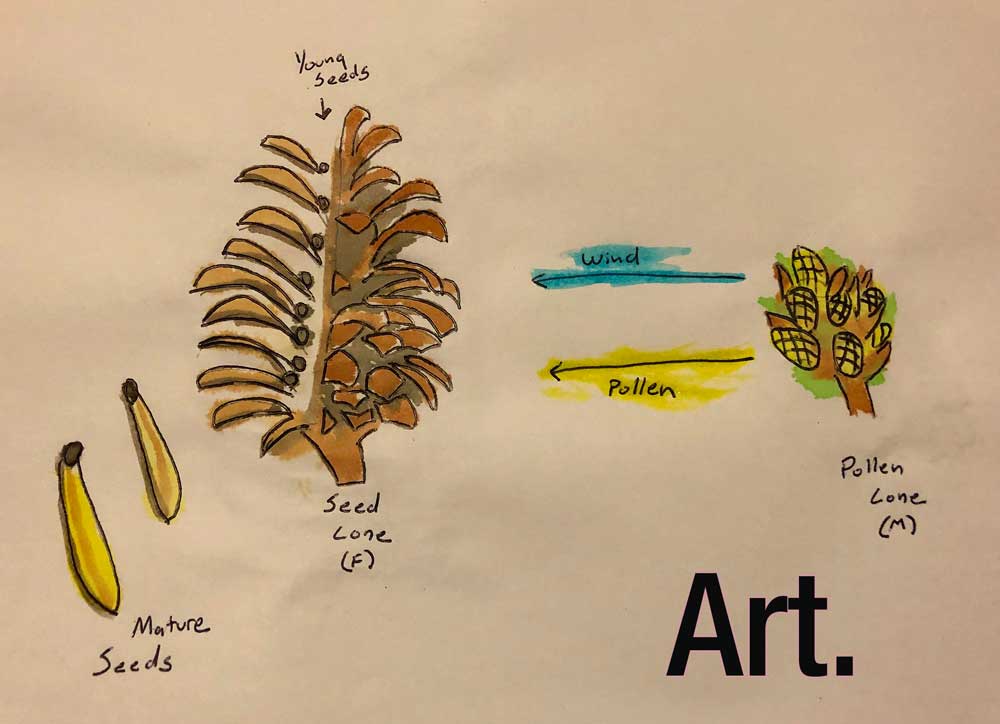



Outdoor Education School Science Camps California




Flowering Plant Life Cycles Science Learning Hub




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow




Complex Body Seed Reproduction Flowering Angiosperms Stock Photo Edit Now




Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Fertilization Youtube
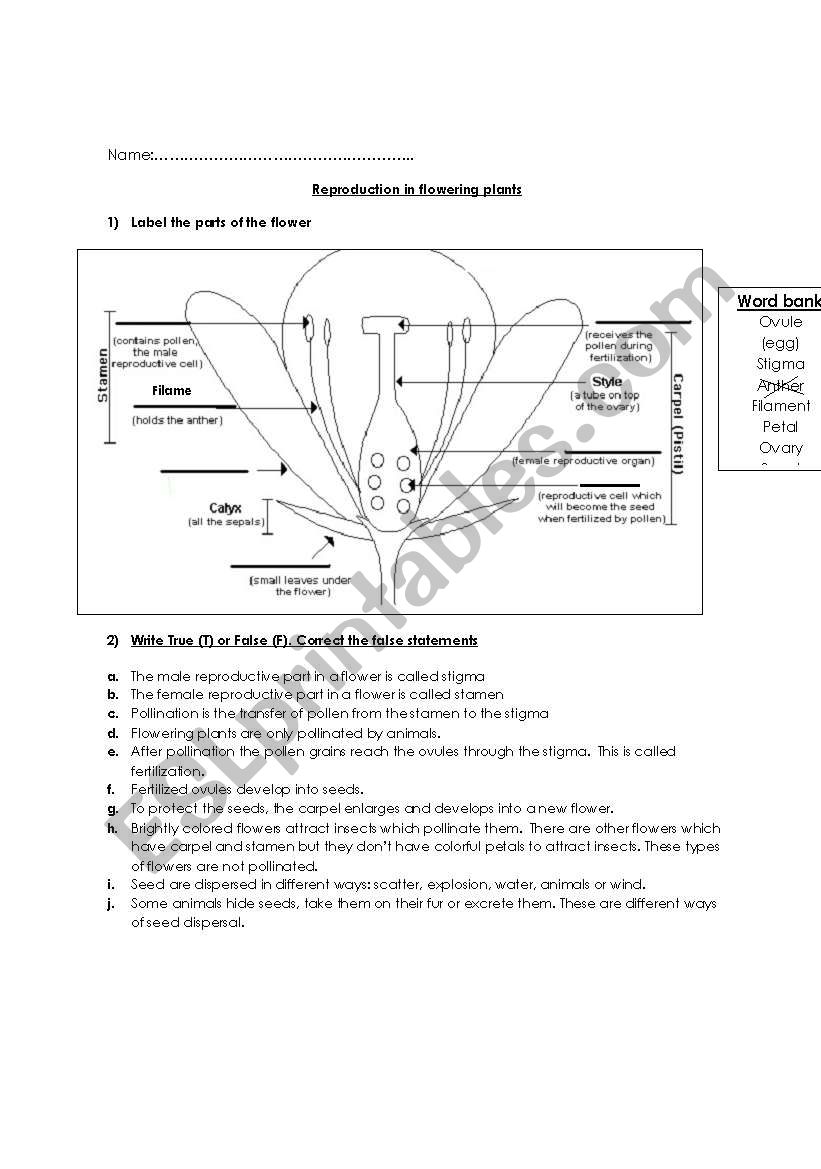



Reproduction In Flowering Plants Worksheet 1 Esl Worksheet By Eicristin



3




Science Unit 3 Lesson 2 Review Flashcards Quizlet



Reproduction In Flowering Plants Presentation Biology
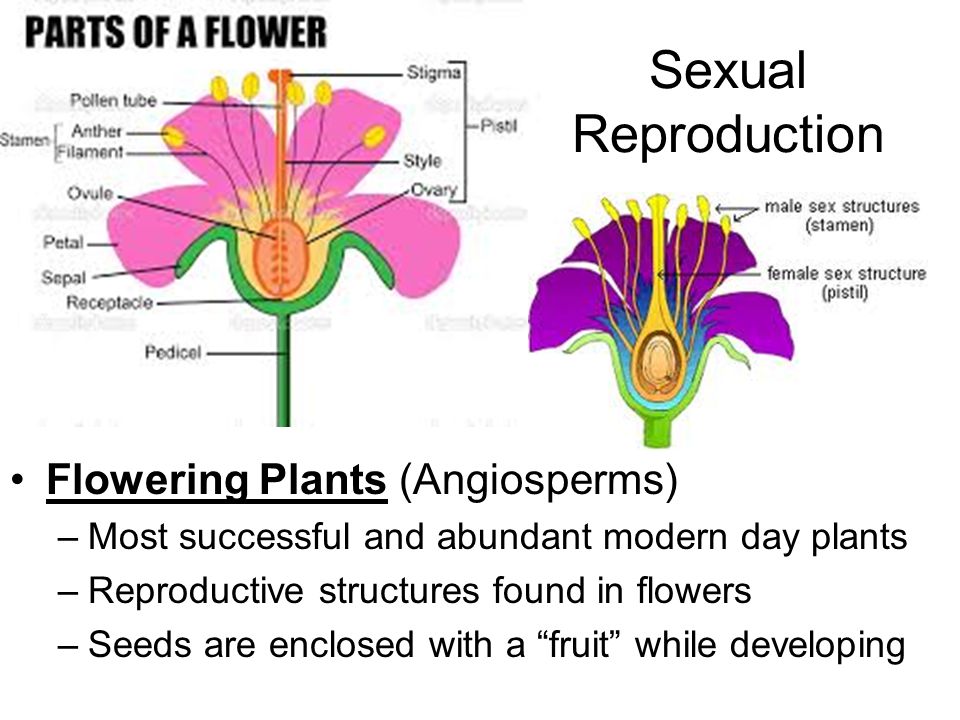



Plant Reproduction Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants 3 Min Ppt Video Online Download
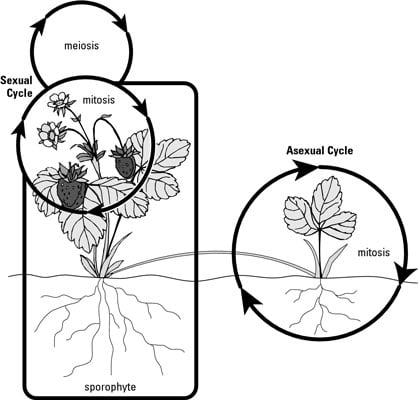



Plant Reproduction Dummies



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Dk Science Seed Plants




How Do Flowering Plants Reproduce c Bitesize




The Plants By Ceipsantaana1 Issuu




Seed Bearing Plants Science Learning Hub




Nova The Reproductive Role Of Flowers Pbs Learningmedia




13 3 Sexual Reproduction In Seed Plants



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Reproduction In Flowering Plants




Plants Iii Vascular Flowering Plants Biol110f13 Confluence




Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Ppt Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
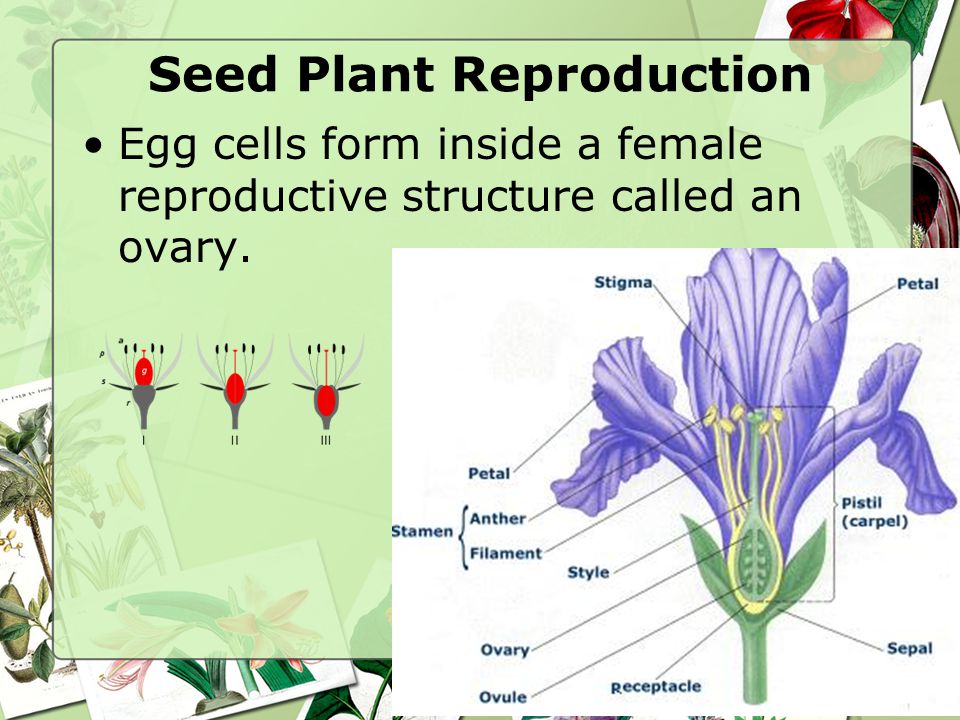



3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download



1
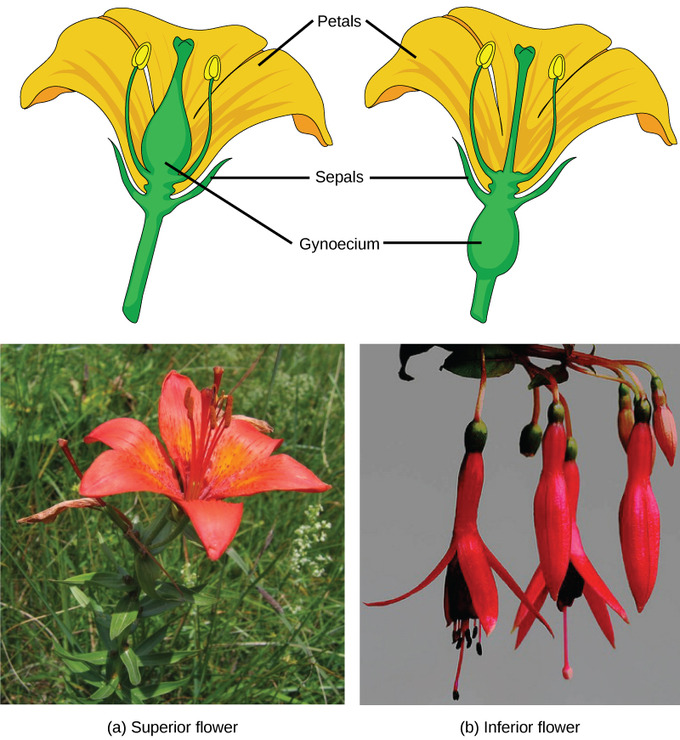



Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Boundless Biology




Learn About Flowering Plant Reproduction Chegg Com




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow
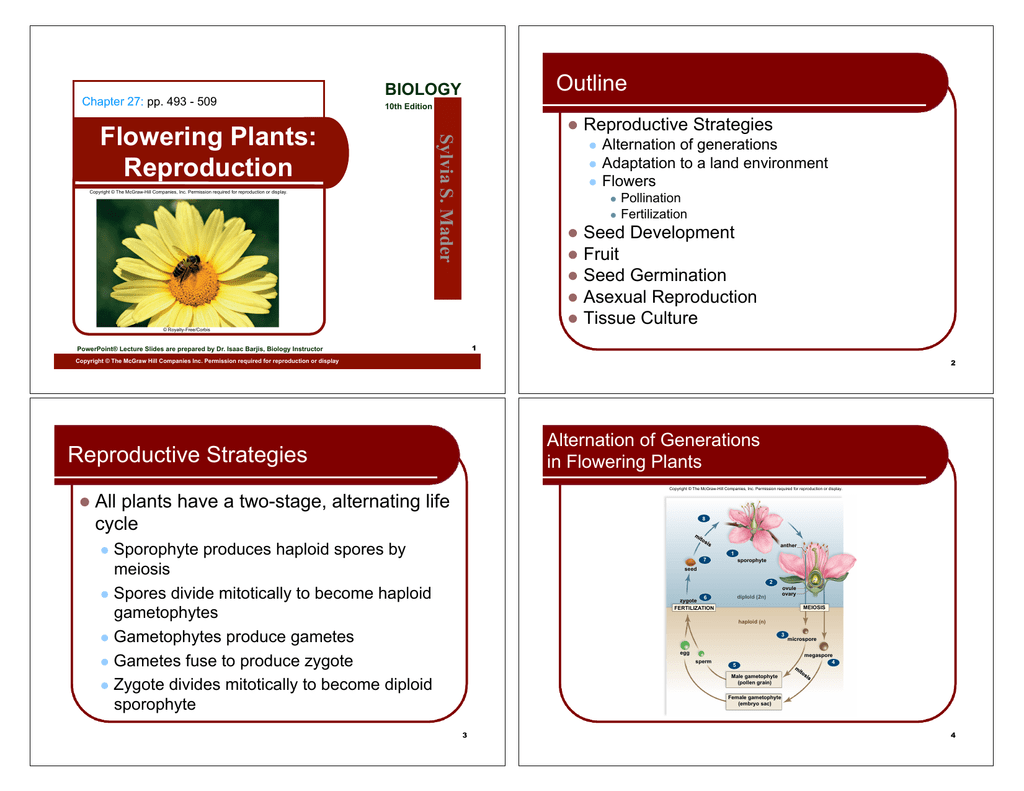



Flowering Plants Reproduction
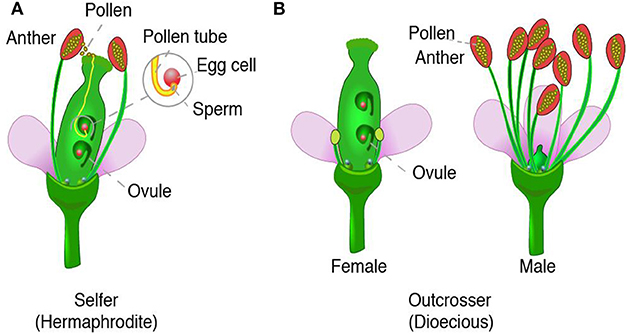



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Ppt Plant Reproduction Flowers Fruits And Seeds Powerpoint Presentation Id




Plant Reproductive System Angiosperms Britannica




Flowering Plant Wikipedia




How Flowering Plants Reproduce Students Britannica Kids Homework Help




Short Notes Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants School




Flowers Or Flowers X28 Latin Flos X29 Is A Means Of Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Stock Photo Image Of Sexual Means



1




Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants Youtube



Flowering Plant Reproduction




More On Morphology Of The Anthophyta



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿